In-Utero Puppy Development & Placental Health: A Complete Guide for Dog Breeders
fetal development of puppies
How puppies attach and connect in utero
1. Implantation process
Around 18–20 days after the LH surge, blastocysts attach centrally on the uterine wall (antimesometrial side) and begin implantation.
The trophoblast (outer layer of embryonic cells) produces enzymes that erode the maternal endometrium, letting it embed close to maternal blood vessels.
2. Zonary, endotheliochorial placenta
Dogs develop a zonary placenta, shaped like a band encircling each fetus within the uterine horn.
It’s endotheliochorial: fetal chorionic cells contact maternal endothelial cells (vessel lining) beneath the uterine epithelium.
3. Formation and structure
As the placenta forms, you’ll see a green-brown “marginal hematoma”—a blood-rich zone at the edge of the placental band.
Inside the placenta, a labyrinth of fetal vessels within the chorioallantoic membrane develops, through which nutrient, gas, and waste exchange occurs.
4. Umbilical cord connection
An umbilical cord forms, connecting the fetus (inside its amniotic sac) to the placenta, transferring nutrients and oxygen from the mother’s blood.
5. At birth
The placenta detaches across the junctional zone and is delivered after each puppy — the mother often removes the sac and chews the cord.
Summary
Blastocyst implants ~day 18–20.
Trophoblast erodes the uterine lining to form the zonary placenta.
The placenta surrounds the fetus with a vascularized interface and a hematoma.
The fetus connects via the umbilical cord to the placenta.
At parturition, the placenta detaches and is expelled.
Puppy Fetal Development (Week by Week)
| Developmental Stage | Timeline | Key Milestones |
|---|---|---|
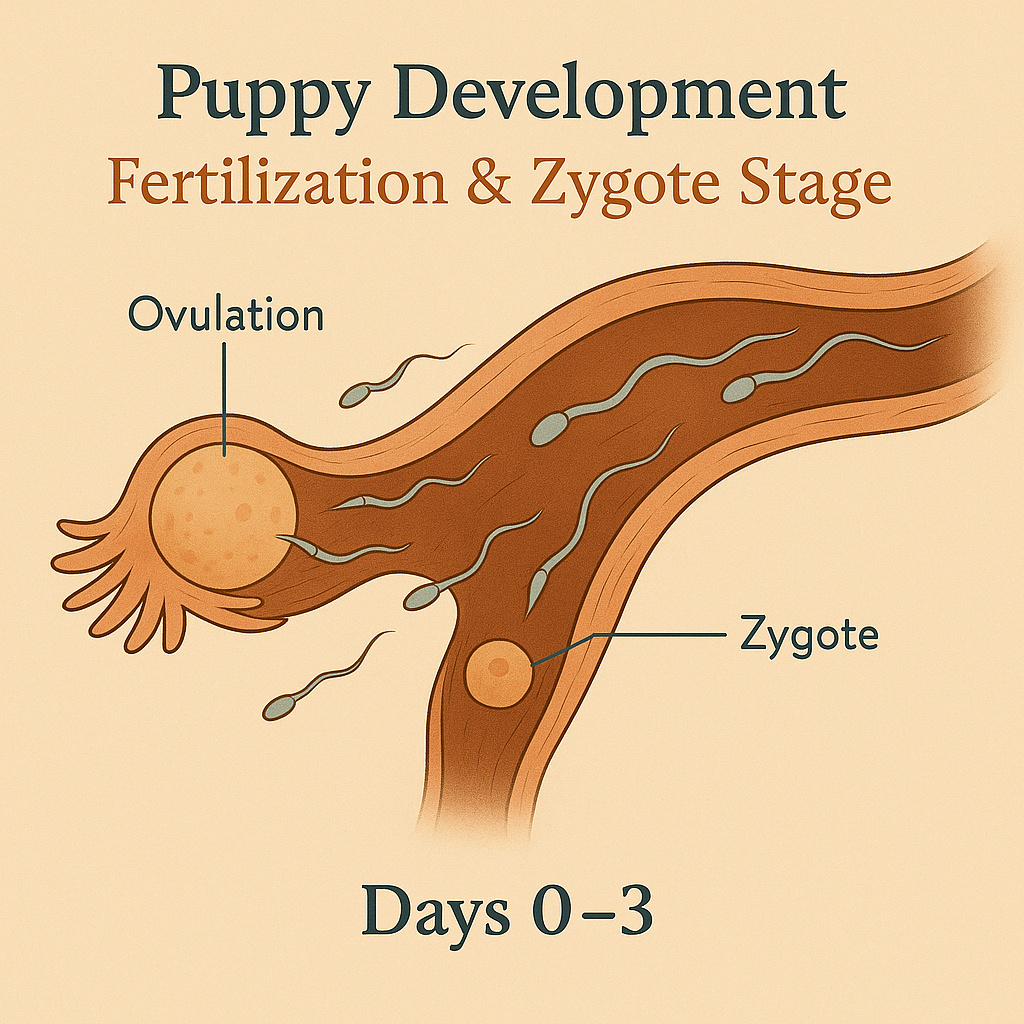
| Fertilization & Zygote Formation | Days 0–3 | Ovulation occurs; sperm meets egg in oviduct; zygote begins rapid cell division |
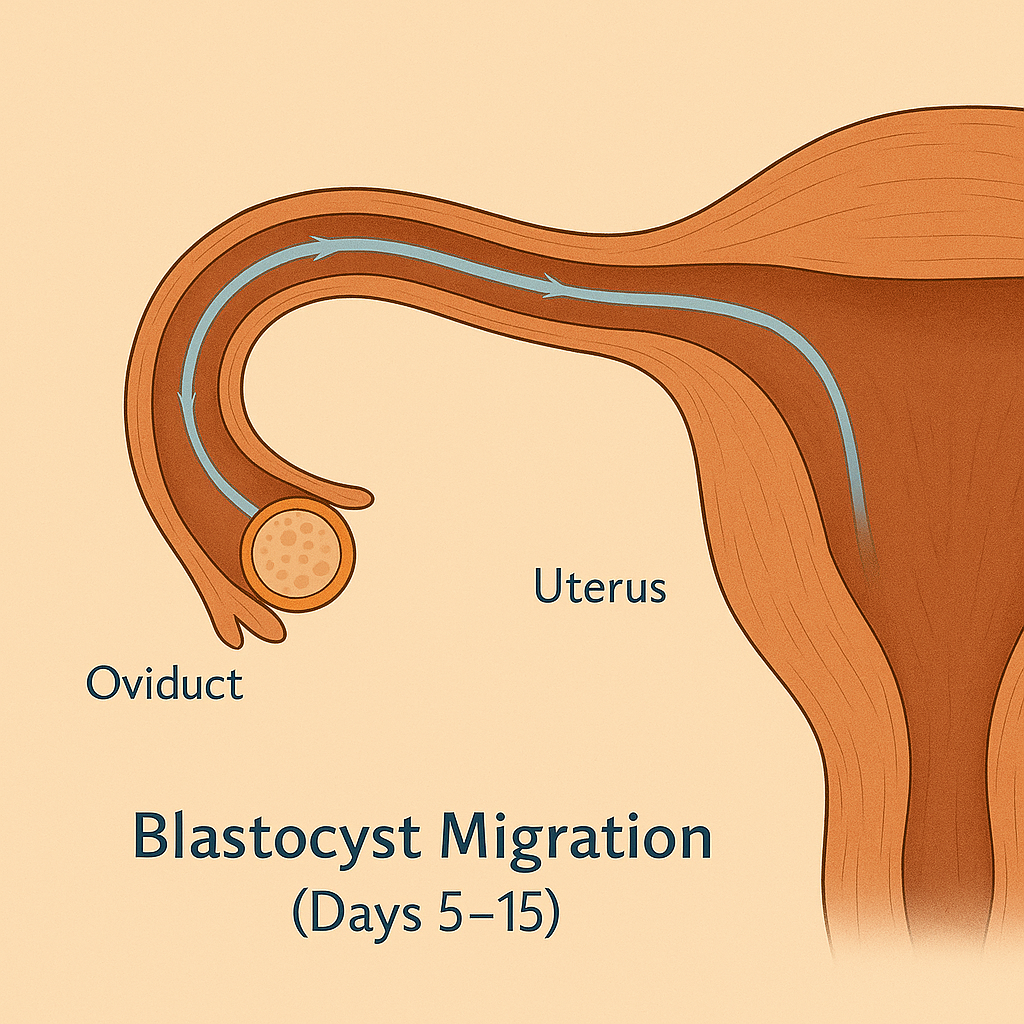
| Blastocyst Migration | Days 5–15 | Embryos travel through uterine horns, forming protective outer layer |
| Implantation | Days 17–21 | Blastocysts embed into uterine lining; early placenta begins forming |
| Placental Development | Days 21–28 | Zonary placenta forms; nutrient exchange begins; basic body systems emerge |
| Organogenesis | Weeks 3–4 | Major organs develop; spine, head, limbs, and facial structures become visible |
| Mid-Gestation Growth | Weeks 5–6 | Skeleton begins ossifying; gender becomes visible via ultrasound; puppies grow rapidly in length |
| Late Gestation & Whelping Readiness | Weeks 7–9 | Hair and pigmentation develop; puppies crowd the uterus; lungs mature; birth is imminent |
Understanding the prenatal journey of puppies helps breeders support healthy pregnancies and anticipate key milestones. Below is an overview based on first breeding (Day 0) toward the average 63-day gestation (range: 59–70 days).
Week 1 (Days 1–7)
What’s happening: Fertilization occurs; embryos are 2–4 cells deep, moving through the oviduct.
Dam’s signs: Subtle—possibly mild fatigue, no overt pregnancy changes; heat cycle continues for another 4–14 days.
Week 2 (Days 8–14)
Embryo development: Cell division continues—embryos reach the 64-cell stage and enter the uterine horns.
Dam’s signs: Behavior and appetite likely unchanged; breeders should still manage male access and maintain her normal routine.
Week 3 (Days 15–21)
Implantation: Embryos embed into the uterine lining around Days 17–22; the placenta begins forming (~Day 18).
Embryo becomes complex: By the end of week, head, spine, and early organ systems begin to develop.
Dam’s signs: May show slight appetite changes or mood shifts, though often still unremarkable.
Week 4 (Days 22–28)
Fetal milestones (5–17 mm): Head shifts forward, brain and facial features begin, spinal cord forms, initial eyes appear, limb buds emerge.
Diagnostics: Ultrasound can often detect a heartbeat from Day 25 onward; palpation may also be possible in experienced hands.
Dam’s signs: Slight appetite loss (“morning sickness”), nipple enlargement, potential mild discharge.
Weeks 5–6 (Days 29–42)
Puppy features: By Day 35, embryos transition to recognizable fetuses—claws, whisker buds, digit formation, eyelids closed by Day 32–35; fetal length ~30–45 mm, weight ~2–6 g
Fetal heartbeats are detectable with a stethoscope; skeletal ossification begins
Dam care: Nutritional needs rise—start gradual food increase and transition to growth diet; abdomen visibly expanding; nipples darken, mammary gland secretions may begin.
Weeks 7–8 (Days 43–56)
Rapid growth: Skeleton fully ossified by Day 50—puppy bone structure visible on X-ray; coat beginnings, pigmentation, proportional development continue; fetal movement can be felt.
Dam signs: Reduced appetite, heavier abdomen, nesting behavior; milk production (“first milk”) may appear.
Breeder tasks: Perform X-ray to confirm litter size; finalize whelping area and gather supplies.
Week 9 (Days 57–63+)
Final prep: Puppies gain last ounces; full-term between Days 58–65, though larger litters may come early; some may extend to Day 70 from breeding due to ovulation timing.
Dam signs: Nesting intensifies, restlessness rises, and appetite may drop. Monitor temperature for drop to ~100 °F (37.8 °C) — whelping likely within 24 hours.
Outcome: Puppies born blind and deaf—their senses, eyes, and ears develop postnatally.
REFERNCES
Elanco Animal Health. (n.d.). Week by week guide to dog pregnancy. Retrieved June 24, 2025, from https://www.elanco.com
Baldivis Vet Hospital. (2022). Gestation in dogs – week by week. Retrieved June 24, 2025, from https://www.baldivisvet.com.au
American Kennel Club. (2021, April 5). Dog pregnancy: Signs, care, and preparing for puppies. Retrieved June 24, 2025, from https://www.akc.org/expert-advice/health/dog-pregnancy-signs-care/
Luv-N-Care Animal Hospital. (2020). Fetal development of a puppy. Retrieved June 24, 2025, from https://www.luvncare.net/fetal-development-of-a-puppy.pml
Veterinary Partner (VIN). (2020). Pregnancy and parturition in dogs. Retrieved June 24, 2025, from https://veterinarypartner.vin.com
Royal Veterinary College. (n.d.). Prenatal development in the dog. eMedia Unit. Retrieved June 24, 2025, from https://emedia.rvc.ac.uk
Puppy Midwife. (2023). Dog pregnancy calendar. Retrieved June 24, 2025, from https://www.puppymidwife.com/dog-pregnancy-calendar
Concannon, P. W. (2011). Reproductive cycles of the domestic bitch. Animal Reproduction Science, 124(3–4), 200–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anireprosci.2010.08.028